Your cart
There are no more items in your cart
- News
- 162975 views
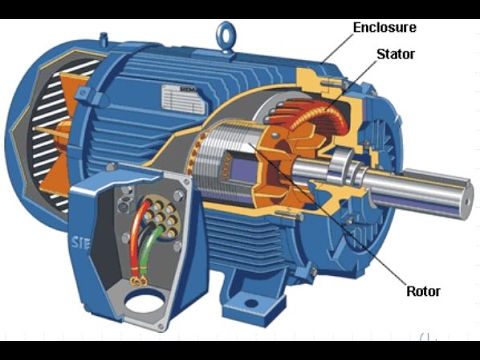
The generator is a rotating machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. There are several types of generators: synchronous and asynchronous. Today in our article we are going to give you more information about each one of them so that you can better understand its operation and its possible uses.
Both generators are made up of a stator (fixed part) and a rotor (moving part). The difference between synchronous and asynchronous motors lies in the rotor:
Has this article been useful to you? Do you need our advice to find what you have been looking for for a long time? Write us or call us! We will be happy to help you.
